Assessment of Beating Paramaters in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Enables Quantitative in Vitro Screening for Cadiotoxicity
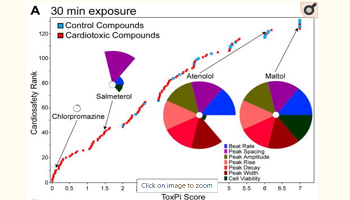
Human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived cardiomyocytes show promise for screening during early drug development. Here, we tested a hypothesis that in vitro assessment of multiple cardiomyocyte physiological parameters enables predictive and mechanistically-interpretable evaluation of cardiotoxicity in a high-throughput format. Human iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes were exposed for 30 min or 24 h to 131 drugs, positive (107) and negative (24) for in vivo cardiotoxicity, in up to 6 concentrations (3 nM to 30 uM) in 384-well plates. Fast kinetic imaging was used to monitor changes in cardiomyocyte function using intracellular Ca(2+) flux readouts synchronous with beating, and cell viability.